Program Lead
Abu Bakar Siddik
Our Approach
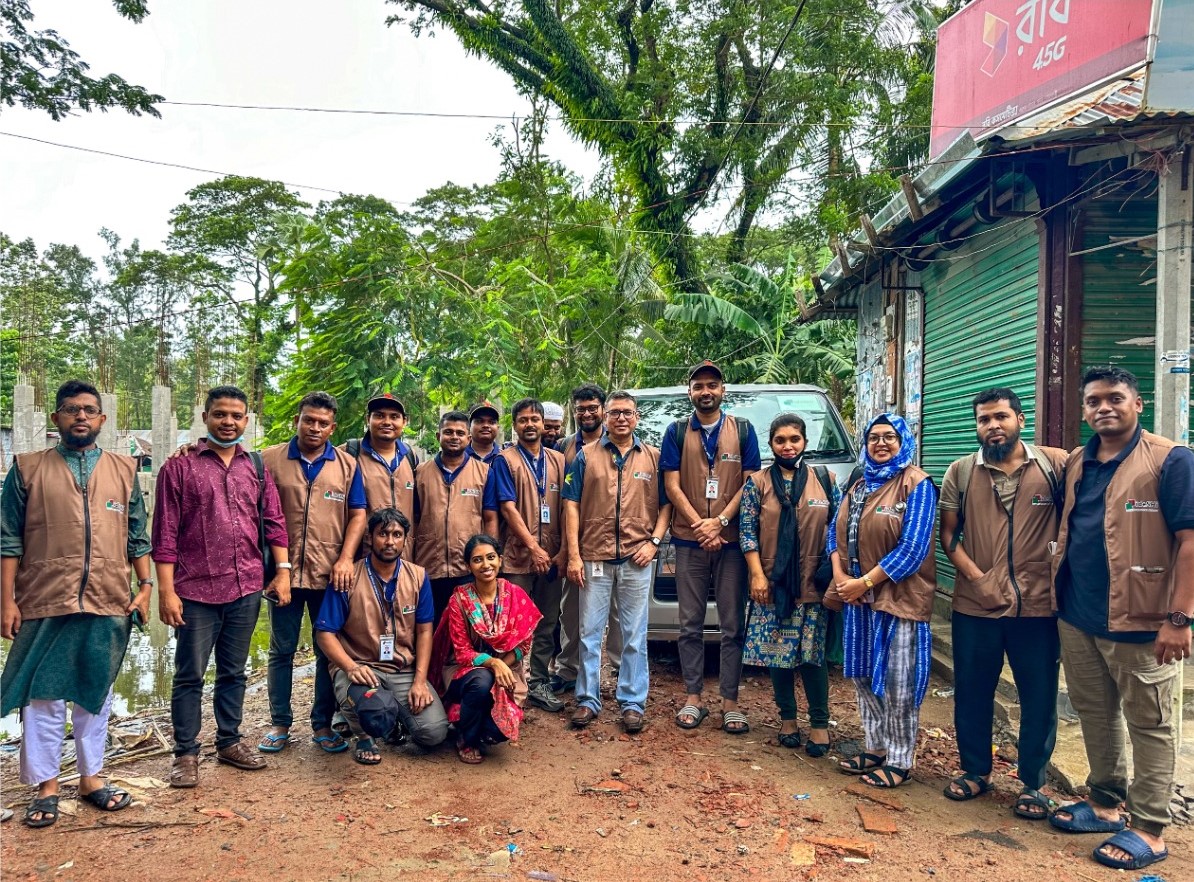
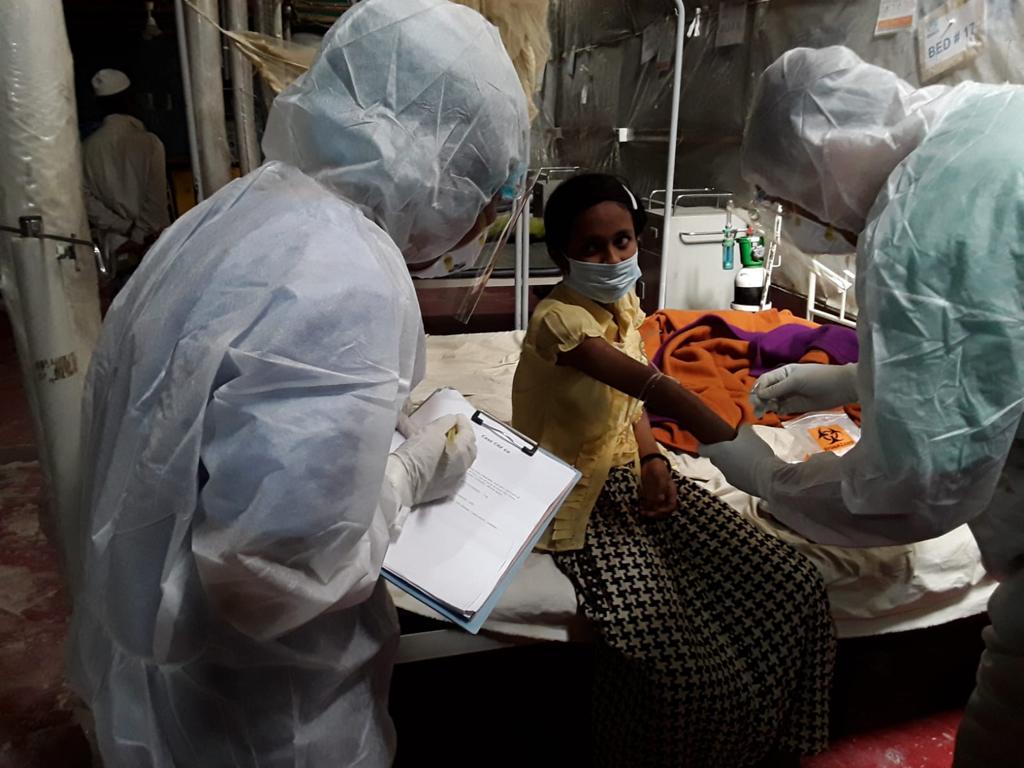
As part of our ongoing efforts to contain the COVID-19 pandemic since it first started in 2020, we have extended our research to include the forcibly displaced Myanmar nationals (FDMN)also as known as Rohingya population in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Recognizing the unique challenges that this vulnerable community faces, we have begun a comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 serology surveillance study among Rohingya refugees. Understanding the serological responses, particularly IgG antibodies, among FDMNs after natural infection and vaccination up to a year of follow-up will aid in vaccination strategies and public health awareness.
Partners
Mérieux Foundation, France and ideSHi
Research Goals
Through the study, we aim to identify the duration and strength of IgG antibody responses following natural infection as well as vaccination, which will be crucial in determining the timing and necessity of vaccine doses among the FDMN community.
Context
The COVID-19 pandemic has emerged as a global threat, affecting communities worldwide. Incorporating the population of forcibly displaced Myanmar nationals (FDMN) into these serology studies is crucial, as these marginalized individuals, living in challenging conditions, represent a unique demographic.
By including them in studies, we can learn more about how COVID-19 impacts communities that are already at risk. Research on serology, particularly concentrating on IgG antibody responses, is essential to comprehending immunity against COVID-19. IgG antibodies are vital indicators that aid in the identification of previous infections and help formulate immunization programs to ensure population-wide immunity. This research offers vital information regarding the duration and breadth of antibody response upon natural infection as well as vaccination which will be crucial in public health decision making and vaccination policy determination against the pandemic.
Impact
By ensuring more effective protection against COVID-19 within this marginalized community, the serology study among FDMN will aid in the development of public health policies and vaccination strategies. Furthermore, it will enhance our understanding of how the pandemic affects vulnerable populations, allowing for a more comprehensive global response in such crisis situations